AR Chart: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the complexities of time series data can be quite challenging, especially when it comes to visualizing patterns and trends. One of the most effective tools for this purpose is the AR chart. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of AR charts, exploring their construction, interpretation, and applications in various fields. So, let’s embark on this journey of discovery and uncover the secrets hidden within AR charts.
What is an AR Chart?

An AR chart, short for Autoregressive chart, is a graphical representation of a time series data that illustrates the relationship between the current value and its past values. It is a valuable tool for identifying patterns, trends, and cycles within the data. By analyzing the AR chart, you can gain insights into the underlying structure of the time series and make more informed predictions about its future behavior.
Constructing an AR Chart
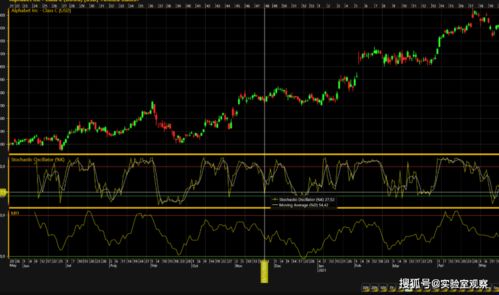
Constructing an AR chart involves several steps. Here’s a brief overview of the process:
-
Collect the time series data: Begin by gathering the time series data you want to analyze. This could be anything from stock prices, temperature readings, or sales figures.
-
Calculate the lagged values: Lagged values are the past values of the time series data. For example, if you have daily stock prices, the lagged values would be the stock prices from the previous day, two days ago, and so on.
-
Calculate the correlation coefficients: The correlation coefficients measure the strength and direction of the relationship between the current value and its lagged values. You can calculate these coefficients using statistical software or programming languages like Python or R.
-
Plot the AR chart: Once you have the correlation coefficients, you can plot the AR chart. The x-axis represents the lagged values, while the y-axis represents the correlation coefficients.
Here’s an example of an AR chart:
| Lagged Values | Correlation Coefficients |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.8 |
| 2 | 0.6 |
| 3 | 0.4 |
| 4 | 0.2 |
| 5 | -0.1 |
Interpreting an AR Chart
Interpreting an AR chart involves analyzing the pattern and shape of the chart. Here are some key points to consider:
-
Peak and troughs: Look for peaks and troughs in the AR chart. These indicate periods of high and low correlation between the current value and its lagged values.
-
Seasonality: If the AR chart exhibits a repeating pattern, it suggests the presence of seasonality in the data. This can be useful for predicting future trends.
-
Autocorrelation: The strength of the correlation between the current value and its lagged values is known as autocorrelation. A high autocorrelation indicates that past values have a significant impact on the current value.
Applications of AR Charts
AR charts have a wide range of applications across various fields. Here are some examples:
-
Finance: AR charts can be used to analyze stock prices, identify trends, and make predictions about future market movements.
-
Weather forecasting: AR charts can help meteorologists predict weather patterns and forecast future weather conditions.
-
Energy consumption: AR charts can be used to analyze energy consumption patterns and predict future energy demands.
-
Healthcare: AR charts can be used to analyze patient data, identify trends, and make predictions about patient outcomes.
In conclusion, AR charts are a powerful tool for analyzing time series data. By understanding the construction, interpretation, and applications of AR charts, you can gain valuable insights into the patterns and trends hidden within your data. So,