Understanding the AR Verb Conjugation Chart: A Detailed Guide for You
When delving into the world of Spanish, one of the most crucial aspects to master is verb conjugation. The AR verbs, also known as irregular verbs, can be particularly challenging due to their unpredictable behavior. In this article, I will provide you with a comprehensive guide to the AR verb conjugation chart, ensuring that you have a thorough understanding of how to conjugate these verbs correctly.
What are AR Verbs?
AR verbs are a group of irregular verbs in Spanish that do not follow the standard conjugation patterns. They are called AR verbs because the stem of these verbs typically ends in “ar.” Some common examples of AR verbs include “hablar” (to talk), “comer” (to eat), and “vivir” (to live).
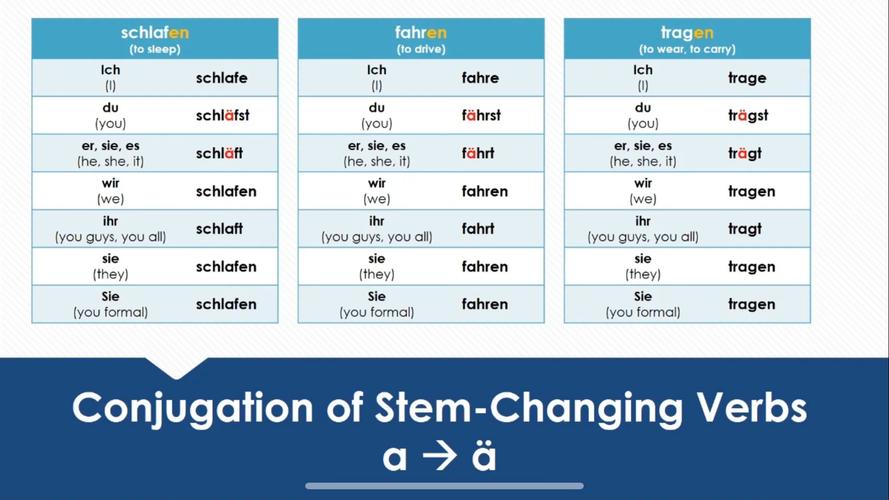
The AR Verb Conjugation Chart
The AR verb conjugation chart is a visual representation of the different forms of AR verbs in the present tense. It includes the stem of the verb and the endings that are added to form the different conjugations. Below is a table showing the AR verb conjugation chart for the present tense:
| Subject | Verb Stem | Ending | Conjugation |
|---|---|---|---|
| yo | hablar | o | hablo |
| t煤 | hablar | as | hablas |
| 茅l/ella/usted | hablar | a | habla |
| nosotros/nosotras | hablar | amos | hablamos |
| vuestra/su | hablar | an | hablan |
As you can see from the table, the endings vary depending on the subject. The stem of the verb remains the same, while the endings change to match the subject. This pattern is consistent across all AR verbs in the present tense.
Conjugating AR Verbs in Different Tenses
While the present tense AR verb conjugation chart is essential, it’s important to note that AR verbs can also be conjugated in other tenses. The process of conjugating AR verbs in different tenses is similar to that of regular verbs, but with some exceptions. Here are a few key points to keep in mind:
-
For the preterite tense, the endings are typically “-茅,” “-aste,” “-贸,” “-imos,” “-iste,” and “-ieron.” However, there are exceptions to this rule, and some AR verbs may have unique endings.
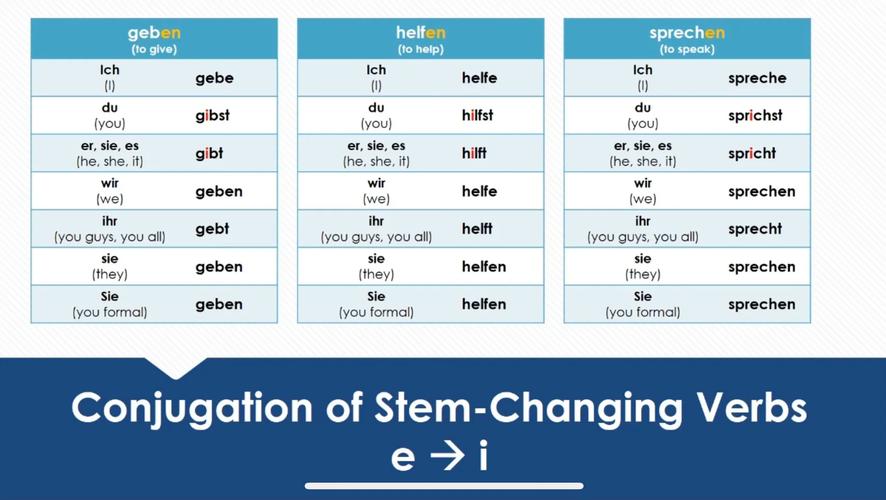
-
The imperfect tense follows a similar pattern, with endings of “-铆a,” “-铆as,” “-铆a,” “-铆amos,” “-铆ais,” and “-铆an.” Again, there are exceptions to this rule.
-
The future tense uses the endings “-茅,” “-谩s,” “-谩,” “-emos,” “-茅is,” and “-谩n,” just like the present tense.
It’s crucial to study each AR verb individually to understand its unique conjugation patterns in different tenses. This will help you avoid making mistakes and ensure that your Spanish is accurate and natural-sounding.
Practice and Resources
Mastering AR verb conjugation requires practice and dedication. To help you along the way, here are some resources and tips:
-
Use online resources and apps that focus on AR verb conjugation. Some popular options include Duolingo, Babbel, and Memrise.
-
Practice conjugating AR verbs in sentences to see how they are used in context.
-
Make flashcards of AR verbs and their conjugations to review them regularly.
-
Seek out a tutor or join
