Ars Disease: A Comprehensive Overview
Ars disease, also known as syphilis, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. It is a significant public health concern worldwide, affecting millions of individuals annually. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of this disease, including its symptoms, transmission, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Understanding the Disease
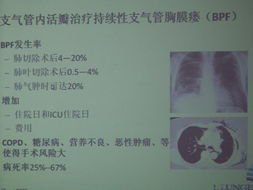
Syphilis has been known since ancient times and was first described by Hippocrates. The disease progresses through four stages: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. Each stage has its own set of symptoms and complications.
| Stage | Symptoms | Complications |
|---|---|---|
| Primary | Single sore (chancre) at the site of infection | None |
| Secondary | Rash, sore throat, hair loss, joint pain, fever, and fatigue | Encephalitis, meningitis, and cardiovascular complications |
| Latent | No symptoms | Neurological and cardiovascular complications |
| Tertiary | Severe neurological, cardiovascular, and skeletal complications | Heart failure, stroke, and dementia |
Transmission of Syphilis
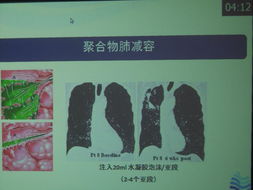
Syphilis is primarily transmitted through sexual contact with an infected individual. The bacterium can enter the body through breaks in the skin or mucous membranes, such as those found in the genitals, rectum, or mouth. It is also possible to contract the disease from an infected mother to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth.
Diagnosis of Syphilis
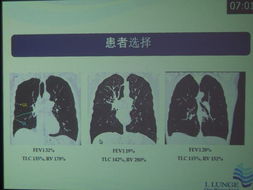
Diagnosing syphilis involves several methods, including blood tests, physical examinations, and sometimes tissue biopsies. The most common blood tests used are the Rapid Plasma Reagin (RPR) and the Treponema pallidum particle agglutination assay (TPPA). These tests detect antibodies produced by the body in response to the infection.
Treatment of Syphilis
Syphilis is curable with antibiotics, primarily penicillin. The treatment regimen depends on the stage of the disease and the individual’s overall health. In some cases, alternative antibiotics may be prescribed for individuals with penicillin allergies.
Prevention of Syphilis
Preventing syphilis involves several strategies, including practicing safe sex, getting regular STI screenings, and using barrier methods such as condoms. Pregnant women should be tested for syphilis to ensure the health of their baby. Additionally, public health campaigns and education programs can help raise awareness about the disease and its prevention.
Impact on Public Health
Syphilis has significant public health implications, particularly in developing countries where access to healthcare and education may be limited. The disease can lead to severe complications, including death, and can also contribute to the spread of other STIs. Efforts to control and eliminate syphilis are essential to protect public health and reduce the burden of this disease on individuals and communities.
Conclusion
Ars disease, or syphilis, is a serious STI that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the disease’s stages, transmission, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention is crucial for individuals and healthcare providers alike. By taking steps to prevent and control syphilis, we can protect public health and reduce the burden of this disease on individuals and communities.
