Understanding TaxPayer: A Comprehensive Guide
As an individual or a business entity, understanding your role as a taxpayer is crucial. TaxPayer, in this context, refers to the person or entity responsible for paying taxes to the government. Taxes are a significant source of revenue for governments, and they fund public services and infrastructure. This article delves into various aspects of being a TaxPayer, including types of taxes, responsibilities, and benefits.
Types of Taxes
There are several types of taxes that individuals and businesses must be aware of. Here’s a breakdown of some common ones:
| Type of Tax | Description |
|---|---|
| Income Tax | Paid by individuals and businesses on their income, which includes salaries, wages, and profits. |
| Corporate Tax | Paid by companies on their profits, which is calculated based on the company’s taxable income. |
| Value Added Tax (VAT) | Collected on the supply of goods and services at each stage of production, and is ultimately paid by the final consumer. |
| Goods and Services Tax (GST) | Similar to VAT, but applicable to a broader range of goods and services. |
| Property Tax | Paid on the value of property owned by individuals or businesses. |
| Excise Duty | Paid on specific goods, such as alcohol, tobacco, and fuel. |
Responsibilities of a TaxPayer
As a TaxPayer, you have several responsibilities, including:
-
Understanding the tax laws and regulations applicable to you.
-
Keeping accurate records of income, expenses, and other financial transactions.
-
Reporting your income and paying taxes on time.
-
Claiming deductions and credits to which you are entitled.
-
Cooperating with tax authorities during audits or investigations.
Benefits of Being a TaxPayer

While paying taxes may seem like a burden, there are several benefits to being a TaxPayer:
-
Public Services: Taxes fund public services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure, which benefit society as a whole.
-
Redistribution of Wealth: Taxes help redistribute wealth from the wealthy to the less fortunate, reducing income inequality.
-
Investment in Future: Taxes contribute to the development of new technologies, industries, and job opportunities.
-
Legal Obligation: Paying taxes is a legal obligation, and failure to do so can result in penalties and legal consequences.
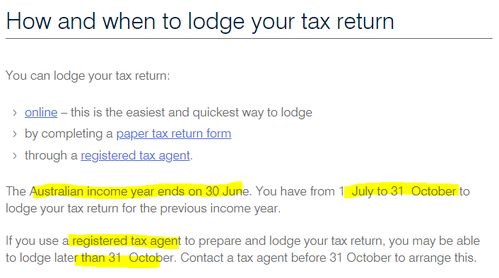
How to File Taxes
Filing taxes can be a daunting task, but it’s essential to do it correctly. Here are some steps to follow:
-
Collect all necessary documents, such as W-2 forms, 1099 forms, and receipts for deductions.
-
Choose the appropriate tax form based on your filing status and income.
-
Fill out the form accurately and double-check your calculations.
-
Submit your tax return by the deadline, either electronically or by mail.
-
Keep a copy of your tax return for your records.
Seeking Professional Help
For many individuals and businesses, seeking professional help with tax preparation is a wise decision. Tax professionals, such as Certified Public Accountants (CPAs) and Enrolled Agents, have the expertise and experience to ensure that your taxes are filed accurately and efficiently. They can also help you navigate complex tax laws and take advantage of available deductions and credits.
In conclusion, understanding your role as a TaxPayer is crucial
